Abstract
Current therapy of CML with tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) aims to achieve a Major Molecular Response to avoid the disease progression to blastic phase and, possibly, a Deep Molecular Response (DMR), to gain the opportunity for TKIs discontinuation and Treatment Free Remission (TFR).
However, TFR strategies are not yet optimized, as well as the criteria for patients (pts) selection to TKI discontinuation are not well defined. The patient's CML prognostic score, the duration of TKI treatment and "stable" DMR before discontinuation and the levels of DMR are still matters of debate.
Due to its intrinsic limitations, RT-qPCR cannot be considered as an optimal tool for a precise detection of minimal BCR-ABL1 transcript levels and DMR monitoring. The digital PCR (dPCR) has emerged as a more sensitive and accurate method to detect and monitor the BCR-ABL1 minimal residual disease (MRD).
This study focused on the BCR-ABL1 RT-q/dPCR comparative monitoring in CML pts treated with TKIs and with durable DMR (≥ 2 years), as conventionally assessed by RT-qPCR, before the enrollment. The aim was to evaluate the reliability and the efficiency of dPCR, as compared to RT-qPCR, for a better identification of "stable" DMR and for a better selection of the candidates for treatment discontinuation.
118 CML pts with durable DMR were enrolled and 493 peripheral blood samples were comparatively analyzed by both RT-qPCR, according to the last International Guidelines, and dPCR (QS3D Digital PCR System). RT-qPCR results were assessed as BCR-ABL1 %IS.
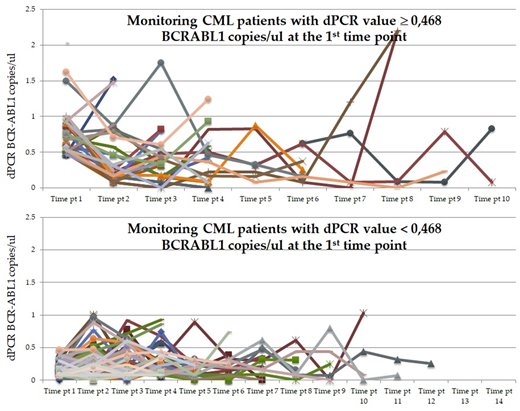
dPCR results were assessed as number of BCR-ABL1 copies/□l of reaction and the molecular response was categorized as □ 0.468 or < 0.468 BCR-ABL1 copies/□l according to the previously reported cut off (Bernardi S. et al, J Mol Biom Diagn, 2017).
Starting from the first RTq/dPCR comparative assessment, the 118 pts were monitored every 3/4 months for at least 3 time points.
Grouping the 118 pts according to the RT-qPCR molecular results at the enrolment, 50 cases (42%) resulted in the MR4.0group and 68 (58%) in the MR 4.5-MR5.0 group. No significant differences were observed between these 2 groups in terms of clinical and hematological characteristics.
At the same time, the 118 pts were divided in 2 groups based on the comparative dPCR molecular results, according to the above mentioned cut-off value: 29 (25%) and 89 (75%) cases had dPCR values □ and □0.468 BCR-ABL1 copies/□l, respectively. No significant clinical differences were observed between these 2 groups.
Out of these 118 pts, 87 (74%) discontinued the TKI treatment and 24 (28%) of them lost the DMR after a median time of 3 months (range 1-30). Based on dPCR, 23/87 (26%) and 64/87 (74%) had dPCR □ 0.468 and < 0.468, respectively. Considering the pts who lost DMR, 12/23 (41%) and 12/64 (20%), had dPCR □ 0.468 and < 0.468, respectively (p=0.0021). Therefore, evaluating BCR-ABL1 transcript levels by dPCR before the discontinuation, we could observe a better TFR (positive predictive value of 80%) in those pts with dPCR < 0.468, with respect to the ones with □ 0.468. However, no significant difference was observed between the groups divided according to the evaluation of BCR-ABL1 transcript levels by RT-qPCR before the discontinuation in terms of TFR prediction.
In order to reach a better recognition of stable DMR, which is strictly related with the probability to achieve and maintain TFR after TKIs discontinuation, we comparatively analyzed, by RTq/dPCR, the course of MRD during the follow up period.
In the case of monitoring by RT-qPCR, a wide oscillation of the molecular responses was observed and they tended to be superimposable both in the group of pts with MR4.0 and in those with MR4.5 and 5.0. In the case of monitoring by dPCR, the values assessed at the enrolment and during the follow up revealed the capability of the dPCR to measure different and heterogeneous numbers of BCR-ABL1 copies in each pts. Moreover, the pts with a dPCR below the cut-off value of 0.468, at enrolment, were maintaining values (median 0,175; range 0-1,863), significantly lower (p<0.0001) than that (median 0,393; range 0-2,195) of the pts with starting values of dPCR above the cut-off of 0.468 (Fig 1).
This retrospective study show that the dPCR is more accurate and sensitive than conventional RT-qPCR for detecting and monitoring the BCR-ABL1 molecular levels and potentially able to improve the recognition of the stable DMR and selection of the candidates to TKI treatment discontinuation.
Bonifacio:Incyte: Consultancy; Pfizer: Consultancy; Amgen: Consultancy; Novartis: Research Funding; Bristol Myers Squibb: Consultancy. Gaidano:Morphosys: Honoraria; Amgen: Consultancy, Honoraria; Janssen: Consultancy, Honoraria; Gilead: Consultancy, Honoraria; Roche: Consultancy, Honoraria; AbbVie: Consultancy, Honoraria. Rossi:Teva: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Mundipharma: Honoraria; Sanofi: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Janssen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Celgene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Abbvie: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Pfizer: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Novartis: Honoraria; Gilead: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Sandoz: Honoraria; Jazz: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Roche: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; BMS: Honoraria; Amgen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Gobbi:Novartis: Consultancy; Ariad: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Pfister: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Amgen: Consultancy; Janssen: Consultancy; Celgene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Voso:Celgene: Research Funding, Speakers Bureau. Abruzzese:Ariad: Consultancy; BMS: Consultancy; Novartis: Consultancy; Pfizer: Consultancy.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal